RapidAML Team
2024-06-18
With the growing significance of Anti-Money Laundering (AML), Countering the Financing of Terrorism (CFT), and Counter-Proliferation Financing (CPF) compliance, it is essential for businesses to develop and adopt a comprehensive AML/CFT/CPF program and ensure its effective implementation. AML software solutions act as strategic tools that help in the smooth, streamlined, and secure implementation of the AML/CFT/CPF program.
This blog explores the function of AML software in automating and optimising the AML/CFT/CPF compliance process for Designated Non-Financial Businesses and Professions (DNFBPs) operating in India. For this purpose, the blog first discusses the meaning and types of DNFBPs and the Indian AML/CFT/CPF regulatory framework applicable to them. Subsequently, the blog elaborates on how AML software solutions can automate and enhance the AML/CFT/CPF compliance process for DNFBPs.
Indian AML/CFT/CPF regulatory regime needs thoughtful navigation by DNFBPs. AML software automates the AML/CFT/CPF compliance process, which may be time-consuming or expensive when done manually. AML software can analyse large amounts of data in real time, to ensure that no element linked with money laundering (ML), terrorism financing (TF), or proliferation financing (PF) enters or misuses the DNFBP.
To understand the role of AML software in the AML/CFT/CPF compliance process in detail, let’s first understand the meaning and types of DNFBPs and the Indian AML/CFT/CPF regulatory regime applicable to them.
Definition of DNFBPs
In India, entities that are required to comply with AML/CFT/CPF laws are referred to as ‘Reporting Entities’ under the Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002 (PMLA). The definition of ‘Reporting Entities’ under PMLA includes certain designated businesses and professions from the non-financial sector.
DNFBPs are those non-financial sector entities that form a major portion of the global economic system. They have been brought within India’s AML/CFT/CPF framework to protect them from the risks of ML, TF, and PF.
DNFBPs covered under PMLA, 2002
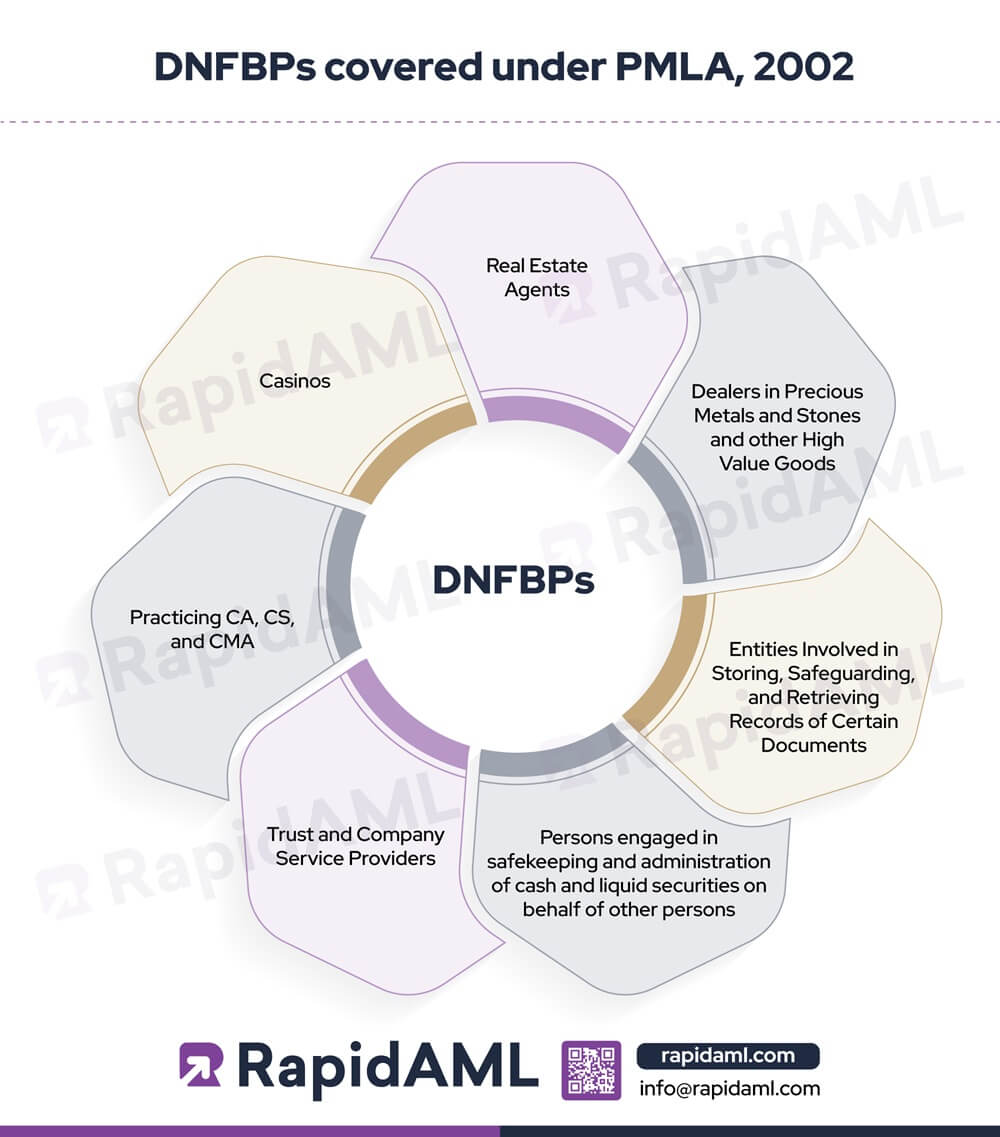
The following DNFBPs are considered ‘Reporting Entities’ under the PMLA and thus subject to AML/CFT/CPF compliance obligations in India:
This category includes any person who provides services for the sale and purchase of real estate and has an annual turnover of ₹20 Lakhs or more.
This includes dealers in precious metals such as gold, platinum, palladium, or rhodium and precious stones such as diamond, emerald, ruby, sapphire, etc., if they engage in cash transactions with a customer equal to or above Rupees 10 lakh, carried out in a single transaction or in several linked operations.
This category includes entities involved in storing, safeguarding, and retrieving records of documents related to transactions in a DNFBP, the identity of their clients and beneficial owners, as well as account files and business correspondence related to their clients.
Persons engaged in safekeeping and administration of cash and liquid securities on behalf of other persons.
This category of entities includes entities conducting activities such as acting as formation agents of companies or Limited Liability Partnerships (LLPs) and providing them with registered offices, business addresses, accommodations, etc. It also includes persons acting as or arranging for another person to act as a director or secretary of the company, a partner of a firm, a trustee of a trust, or a nominee shareholder of another person.
Chartered Accountants, Company Secretaries, and Cost and Works Accountants are considered DNFBPs when they provide services such as buying and selling of immovable property, managing clients’ money, security or other assets, managing clients’ bank, savings or securities accounts, etc.
Persons carrying on activities for playing games of chance for cash or kind, and includes such activities associated with casinos;
Key AML Laws, Regulations, and Guidelines Applicable to DNFBPs in India

Key AML Laws, Regulations, and Guidelines Applicable to DNFBPs in India
Key Regulatory Bodies Regulating AML/CFT/CPF Compliance for DNFBPs in India

AML software is designed to carry out multiple tasks related to the AML/CFT/CPF program to help DNFBPs automate their compliance obligations. By automating compliance, DNFBPs can avoid issues related to conducting AML/CFT/CPF processes manually, such as data not being centralised, slow progress in the completion of compliance tasks, inability to monitor transactions in real time, and high costs of compliance. The components of the AML/CFT/CPF program and how they can be automated through AML software are discussed below.
Know Your Customer (KYC) is a key component of the Customer Due Diligence (CDD) requirements under the PMLA as well as the IFSCA Guidelines. KYC involves the verification of the customer’s identity and facilitates Customer Risk Assessment (CRA). AML software optimises the KYC process in the following ways:
Screening means matching customers’ names with sanctions, Politically Exposed Persons (PEP), and adverse media lists. Sanctions screening involves screening the following sanctions lists:
Screening enables DNPBPs to make informed decisions regarding ML, TF, or PF risks associated with an existing or potential customer. AML compliance can be elevated through screening software in the following ways:
A risk-based approach forms the basis of an AML/CFT/CPF program and is essential for DNFBPs to adopt under the AML/CFT/CPF laws of India. A risk-based approach necessitates analysing ML, TF, and PF risks a DNFBP faces and adopting risk mitigation methods accordingly.
Such risk assessment can be automated through AML software in the following ways:
Transaction monitoring is necessary to ensure that DNFBPs detect and report suspicious transactions to FIU-IND. AML software makes the transaction monitoring process more efficient in the following ways:
Transactions monitoring, ML/TF/PF risk monitoring, or customer risk monitoring is not a one-time process. Monitoring needs to occur on an ongoing basis to ensure that ML, TP, or PF risks do not slip through the cracks. AML software helps in ongoing monitoring in the following ways:
It is mandatory for DNFPBs to submit certain reports to FIU India. Such reports include Suspicious Transaction Report (STR), Cash Transaction Report (CTR), Counterfeit Currency Report (CCR), etc, depending on the type of business it operates. These reports need to be submitted through the FINnet 2.0 Portal of FIU-India. AML software makes this reporting process seamless in the following ways:
The Prevention of Money Laundering Rules (Maintenance of Records) Rules, 2005, as well as IFSCA Guidelines, require DNFBPs to maintain specific documents as part of their AML/CFT/CPF programs. These documents include those collected during the KYC process, transaction records, etc. AML software automates the record-keeping function in the following ways:
Mandated under AML/CFT/CPF laws of India, regular independent audits help identify and remove gaps in the AML program of a DNFB. AML software helps DNFBPs prepare for an independent audit in the following ways:
Conclusion
AML software is a powerful tool for DNFBPs in India and enables them to efficiently meet their AML/CFT/CPF compliance obligations. By automating key components of the AML/CFT/CPF program, DNFBPs can reduce the risk of non-compliance, avoid fines, and maintain the integrity of their operations. Therefore, adopting AML software is a necessity for DNFBPs seeking to protect themselves from ML, TF and PF risks.
Pathik is a Chartered Accountant with over 26 years of experience in governance, risk, and compliance. He helps companies with end-to-end AML compliance services, from conducting Enterprise-Wide Risk Assessments to implementing robust AML compliance frameworks. He has played a pivotal role as a functional expert in developing and implementing RegTech solutions for streamlined compliance.
Pathik's expertise extends to guiding businesses in navigating complex regulatory landscapes, ensuring adherence to FATF and other international standards, and mitigating financial crime risks. He is a recognised thought leader in AML/CFT, frequently sharing insights on emerging compliance challenges on various platforms.
Solutions
Transaction Monitoring
Regulatory Reporting
Services
Industries
Lorem Ipsum
Lorem Ipsum
Lorem Ipsum
Lorem Ipsum
Lorem Ipsum
© RapidAML 2025
Solutions
Transaction Monitoring
Regulatory Reporting
Services
AML/CFT Health Check
Industries
Lorem Ipsum
Lorem Ipsum
Lorem Ipsum
Lorem Ipsum
Lorem Ipsum
© RapidAML 2025
Sign Up Form