
RapidAML Team
2024-06-05
Regulated entities in the UAE are obligated to comply with AML/CFT laws and regulations. Here is the article dealing with the manual and automated approaches for mitigating AML Compliance challenges in UAE.
The UAE has been playing a prominent role in fighting financial crimes. It actively supports the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) and other international organisations’ initiatives to curb the menace of Money Laundering, Financing of Terrorism, or Proliferation Financing (ML/FT/PF) and other crimes. In regard to this, it has laid AML/CFT regulations for:
The AML/CFT laws applying to DNFBPs and VASPs include the following:
Besides these primary laws, their respective regulatory authorities have laid sector-specific guidelines. The UAE’s regulatory authority coordinates and supervises AML/CFT measures in the UAE.
In regard to these AML/CFT laws, the essential requirements include the following:
These AML/CFT requirements align with FATF’s international AML standards and expectations. DNFBPs and VASPs must follow these requirements and take every possible action to fight financial crimes. If they fail to comply, relevant regulatory authority imposes fines and penalties on them. Moreover, they risk their business to money launderers and criminals.
To fulfil the AML/CFT legal obligations, DNFBPs and VASPs need to perform many procedures and processes. These reporting entities are free to decide how they want to comply with the legal requirements. Since these entities are relatively smaller in size and lack proper resources, some of them have resorted to manual processes to comply with their legal obligations. These procedures include the following:
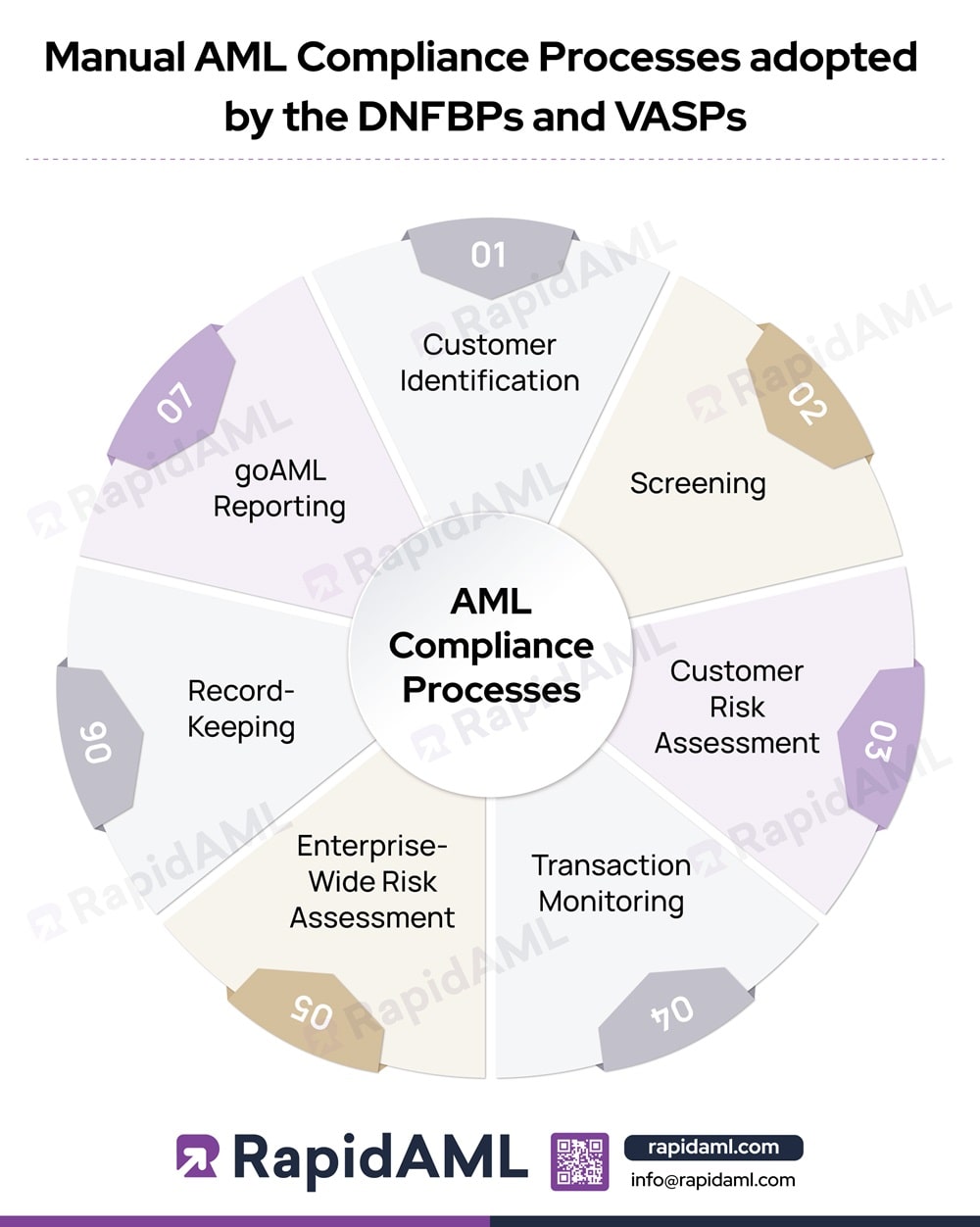
1. Customer Identification
A crucial ingredient of a DNFBP’s or VASP’s AML compliance journey is identifying its customers. They can be individuals or companies. A DNFBP or VASP must make efforts to know who they are. An AML compliance procedure is to collect and verify the following details on customers:
For individuals:
For corporates:
Collecting data concerning customer information is not enough. Carrying out verification is equally essential to ensure that the customer’s identification is valid. For this, a DNFBP or VASP must gather relevant documents from customers:
For individuals:
For companies:
The DNFBP or VASP can verify customers’ identities by relying on third-party sources, such as government databases or credible private sources.
Most of the DNFBPs in UAE use Excel, Word, or PDF templates to capture customer details and maintain them. Some of them also use paper-based forms to capture KYC information. When it comes to VASPs, their customer onboarding processes are mostly automated since they mainly deal with non-face-to-face customers.
2. Screening
Customer screening against sanctions lists and watchlists is a necessary AML compliance procedure. Such screening helps DNFBPs and VASPs identify if their customer features are in any of the sanction lists. These lists include:
Screening entails comparing customers’ names against these lists. If a DNFBP or a VASP finds a match, they are supposed to implement TFS measures such as freezing and suspending business transactions and relationships with such customers. Further, screening against adverse media sources is also recommended. It helps detect negative news about the customer in the media. Thus, all such screening procedures help you better understand your customers and their risks.
The DNFBPs have a choice of downloading these sanction lists from the EOCN website and manually screening the customers. While most of them have subscribed to the screening software, there are DNFBPs still using manual processes to screen their customers in the UAE.
As far as VASPs are concerned, the screening process is more or less automated.
3. Customer Risk Assessment
The KYC and CDD of customers are vital to AML compliance. These help DNFBPs and VASPs create their risk profiles. Based on their identities, documentary proof, and screening results, one can figure out risks associated with a customer. DNFBPs and VASPs are required to check the following before categorising customers as high or low risk:
Before risk profiling, one must also check customers’ historical transactional information. A combination of results from all these enables businesses to score every customer. DNFBPs and VASPs can allocate quantitative scoring to each customer. All this leads to the categorisation of customers into:
Thus, risk categorisation of customers enables one to take a risk-based approach to AML compliance.
Most of the DNFBPs and VASPs have implemented manual processes for the risk categorisation of their customers.
4. Transaction Monitoring
AML compliance requires DNFBPs and VASPs to perform transaction monitoring to spot suspicious ones.
While monitoring transactions, check the following information on customers is considered:
All these details help DNFBPs and VASPs to get to know the customer better. However, before reviewing the transactions, they must know the potential warning signs in their respective industries. These are the red flags that help to spot a suspicious transaction. Red flags also include suspicious customer behaviour while executing the transaction. So, awareness of red flags helps personnel to identify suspicious transactions.
Most of the DNFBPs do not have a mechanism in place to monitor transactions in real time. For some of them due to their nature of business and size, it’s not possible or impractical. However, they would be better off if they automate this process and also have manual oversight.
5. Enterprise-Wide Risk Assessment
Business risk assessment is a recommended AML compliance process for DNFBPs and VASPs. It enables them to identify the money laundering, terrorism financing, and proliferation financing risks to one’s business.
It includes analysis of business lines, product categories, service areas, geographic locations, and distribution channels. The scope of the study also includes all customers, including individuals and corporates, along with the mediums through which transactions are conducted, including physical office, online, and mobile.
All the data collected in KYC, screening, and due diligence are helpful in this stage. Also, historical data on your transactions and customer interactions can help businesses assess and project future risks. Examination of these risks and assigning scores leads to creating a matrix to understand the degree of impact and likelihood of occurrence of a risk. Then, the business can prioritise risks that need to be combatted in which manner, based on the urgency or severity levels, they need to mitigate. DNFBPs and VASPs need to plan actionable strategies to mitigate or prevent these risks.
Most of the DNFBPs and VASPs rely on manual processes to carry out the enterprise-wide risk assessment.
6. Record-Keeping
One often ignored aspect of AML compliance is record-keeping. Documentation, recording, and reporting are all essential to evidence the compliance efforts made by DNFBPs and VASPs in AML compliance. Records of the following processes must be maintained for a prescribed period of time:
These results will help DNFBPs and VASPs to monitor their business further. Reporting to management to aid in decision-making regarding suspicious transactions, activities, and customers to authorities helps in future strategies, actions, and decisions.
Most of the DNFBPs and VASPs maintain soft copies of the transactional documents and records.
7. goAML Reporting
The reporting entities have to submit various reports, such as HRC, HRCA, STR, SAR, DPMSR, and REAR, through the goAML portal. DNFBPs and VASPs maintain manual records for various types of regulatory reporting made with the UAE FIU.
While managing these procedures, DNFBPs and VASPs face several AML compliance challenges like the following:
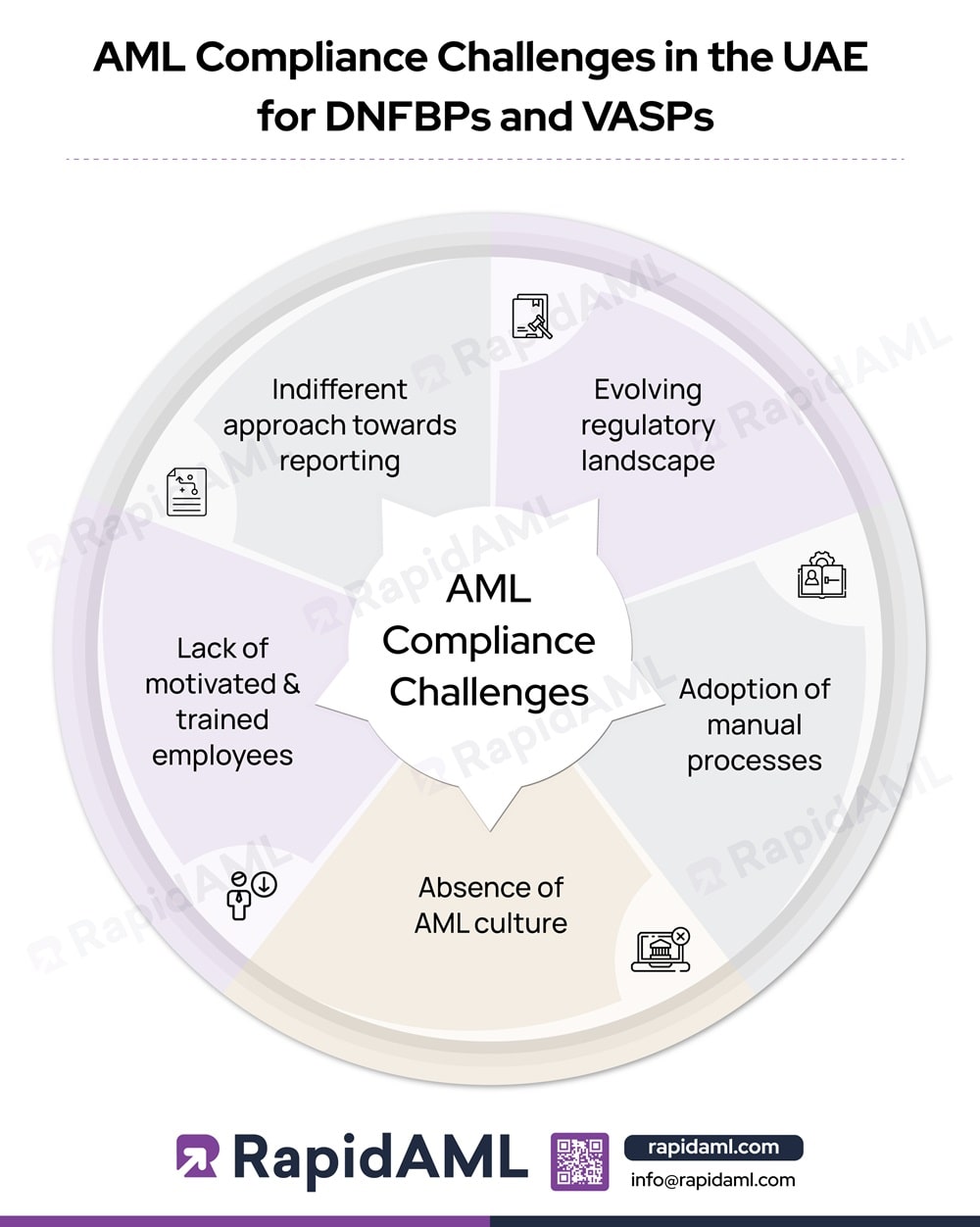
Evolving Regulatory Landscape
Moreover, money launderers and other financial criminals keep innovating their fraudulent practices. They find new avenues of laundering money through legal businesses. The DNFBPs and VASPs must be on their toes at every transaction, customer interaction, and decision. Thus, the evolving regulatory landscape is a critical AML compliance challenge for DNFBPs and VASPs.
It is inevitable for DNFBPs and VASPs to automate various AML compliance processes to keep up with the pace at which regulatory requirements are changing.
Adoption of Manual Processes
Entities need to follow many AML procedures. Each requires dealing with several customers, documents, and data points, which is done manually. Smooth management of all these processes is an enormous AML compliance challenge. And if you manage it all manually, it becomes all the more challenging.
Manual management of KYC, CDD, transaction monitoring, and risk assessment processes can lead to chances of:
These lead to potential non-compliance and reputational and financial loss.
Absence of AML Culture
The creation of an AML culture sets the tone from the top, meaning that right from the senior management to the junior-most employee, everyone is aware of their individual AML/CFT responsibilities. The absence of such a culture can lead to the following:
Lack of Motivated and Trained Employees
Having unskilled AML executives is a severe concern for DNFBPs and VASPs under AML regulations. If they have skills but aren’t motivated, it’s challenging to get the tasks done. So, the lack of motivated, skilled, and trained employees is an AML compliance challenge in the UAE.
The employees must have skills to conduct procedures like:
If they do not possess the skills required to execute these tasks accurately, adequate personnel training for AML/CFT must be organised. Otherwise, the quality of output of these procedures will suffer. Imparting awareness of the latest threats and trends in financial crimes is also essential. Without such knowledge, it will become difficult to ensure an AML compliance culture in its entirety.
Indifferent Approach towards Reporting
Reporting and regulatory communication are essential for DNFBPs and VASPs. When senior management, the AML compliance officer or the Money Laundering Reporting Officer (MLRO) is indifferent towards prompt reporting of suspicious activities and transactions, this results in non-compliance with AML/CFT requirements. Automated tools can help trigger alerts for suspicious patterns observed in transactions and help entities submit regulatory reports in time.
A strategic solution that works wonders for all the AML compliance challenges is the implementation of technology. A software solution can help DNFBPs and VASPs fulfil all the AML compliance requirements per UAE’s AML regulations. Thus, AML compliance automation is what DNFBPs and VASPs need.
The various software features that can help DNFBPs and VASPs with AML compliance procedures are:
The selection of AML compliance software with all these features, either in one solution or separate solutions, will make the compliance process for DNFBPs and VASPs much easier.
One best practice while deploying AML compliance software is integration with the existing systems and processes. For example, the integration of KYC software with the customer onboarding solution improves their efficiency.
Thus, customised, up-to-date, and well-integrated AML compliance software works well for DNFBPs and VASPs on their AML compliance journeys.
Conclusion
Thus, for a smooth ride to legal compliance, DNFBPs and VASPs must overcome AML compliance challenges in the UAE. This will help them adhere to AML regulations and prevent financial crimes.
And all this is possible with the help of AML compliance automation software like RapidAML. With RapidAML, DNFBPs and VASPs can automate AML compliance procedures instead of executing them manually, resulting in the ability to save time, improve accuracy, and complete the process . The ultimate benefit is that DNFBPs and VASPs experience operational efficiency and smooth AML compliance.
Pathik is a Chartered Accountant with over 26 years of experience in governance, risk, and compliance. He helps companies with end-to-end AML compliance services, from conducting Enterprise-Wide Risk Assessments to implementing robust AML compliance frameworks. He has played a pivotal role as a functional expert in developing and implementing RegTech solutions for streamlined compliance.
Pathik's expertise extends to guiding businesses in navigating complex regulatory landscapes, ensuring adherence to FATF and other international standards, and mitigating financial crime risks. He is a recognised thought leader in AML/CFT, frequently sharing insights on emerging compliance challenges on various platforms.
Solutions
Transaction Monitoring
Regulatory Reporting
Services
Industries
Lorem Ipsum
Lorem Ipsum
Lorem Ipsum
Lorem Ipsum
Lorem Ipsum
© RapidAML 2025
Solutions
Transaction Monitoring
Regulatory Reporting
Services
AML/CFT Health Check
Industries
Lorem Ipsum
Lorem Ipsum
Lorem Ipsum
Lorem Ipsum
Lorem Ipsum
© RapidAML 2025
Sign Up Form