Screening
Perform Sanctions, Adverse Media, and PEP Checks with Our Powerful, Next-Gen Screening
Knowledge is Power! So why not have it all?
Get access to 700+ global watchlists, sanctions screening, adverse media and PEP checks, all sharper than a lawyer in a courtroom showdown. Cutting corners? Not our style.
Here’s what we serve with our AML screening software: Segregated results, seamless case management and a treasure trove of premium features.
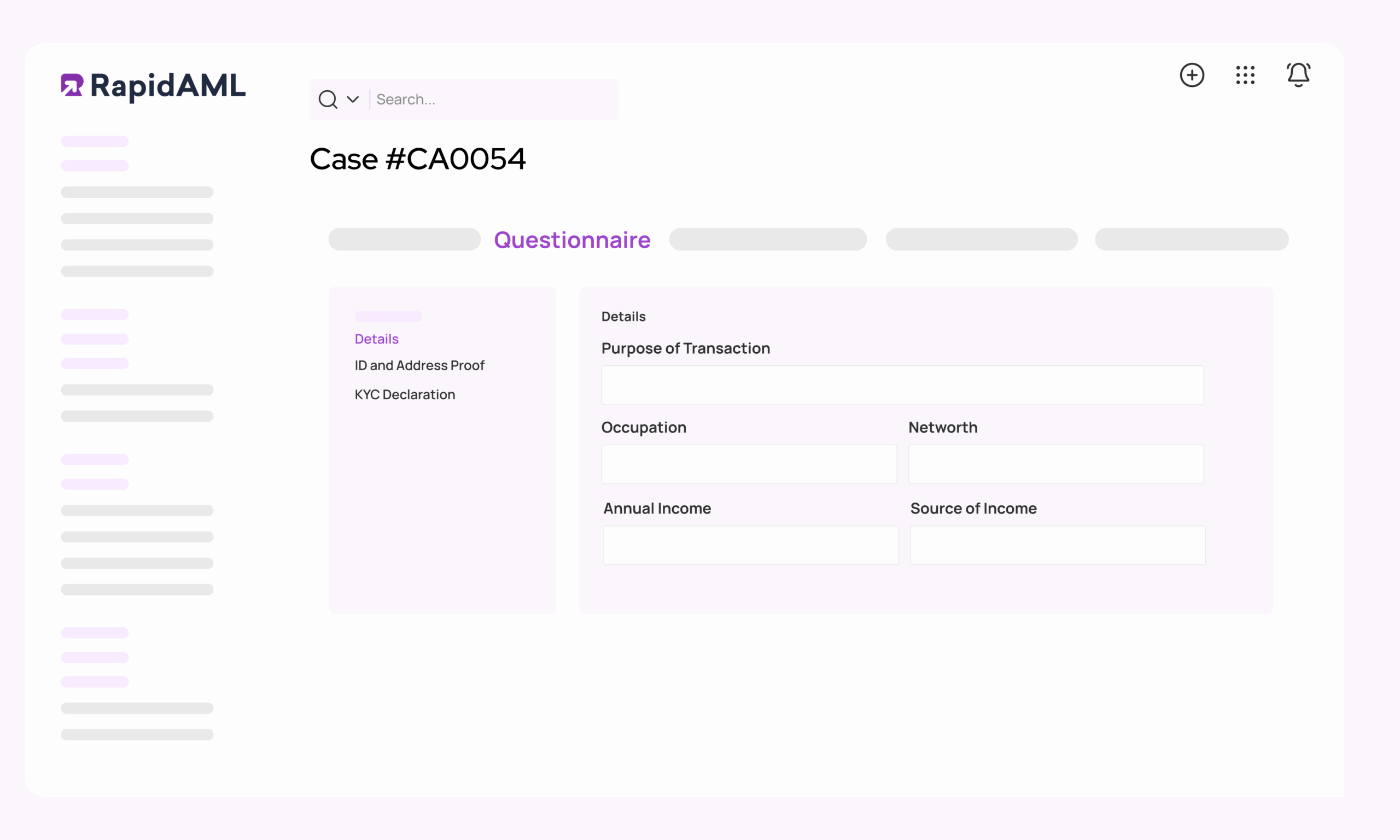
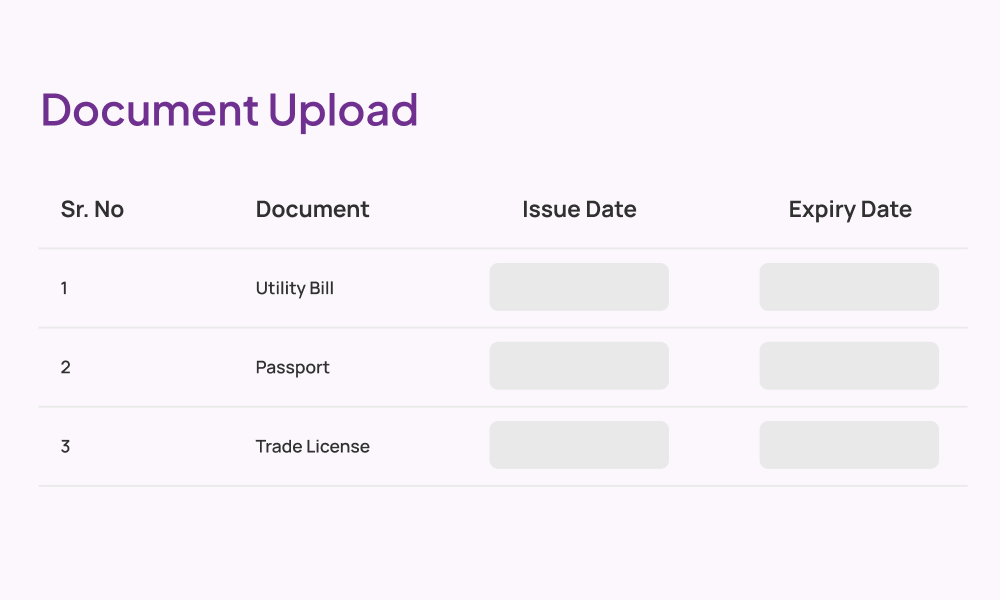
KYC
Experience KYC, The Easy-Peasy Way
With RapidAML, you get smooth KYC management, smoother than your morning coffee.
Secure uploads, easy verification, and storage so safe that even Fort Knox would be jealous. With our AML KYC software, customise your KYC questionnaire to fit like a glove but with automatic reminders for document expiry and refresh. Keep everything ticking like clockwork with the help of our best AML KYC software.
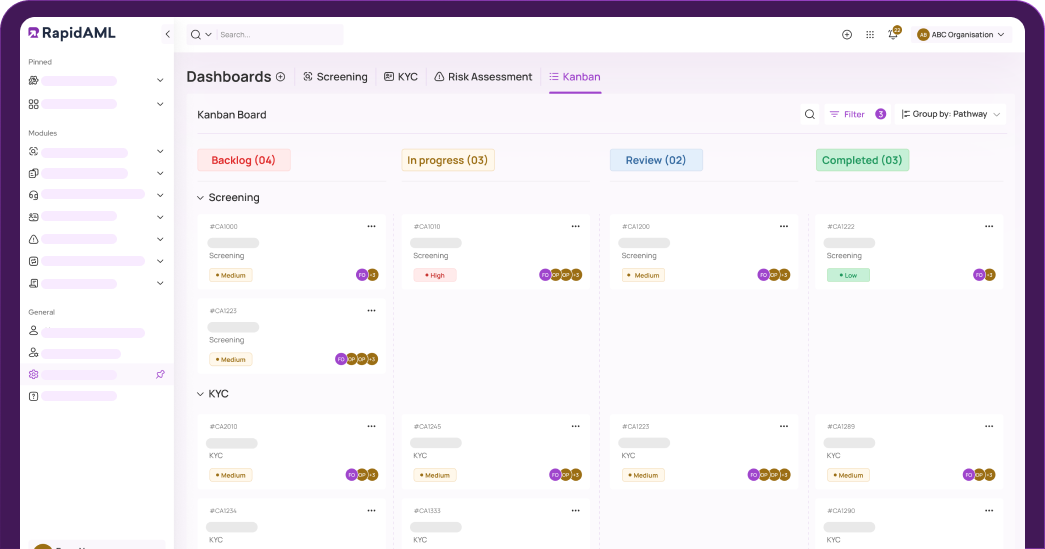
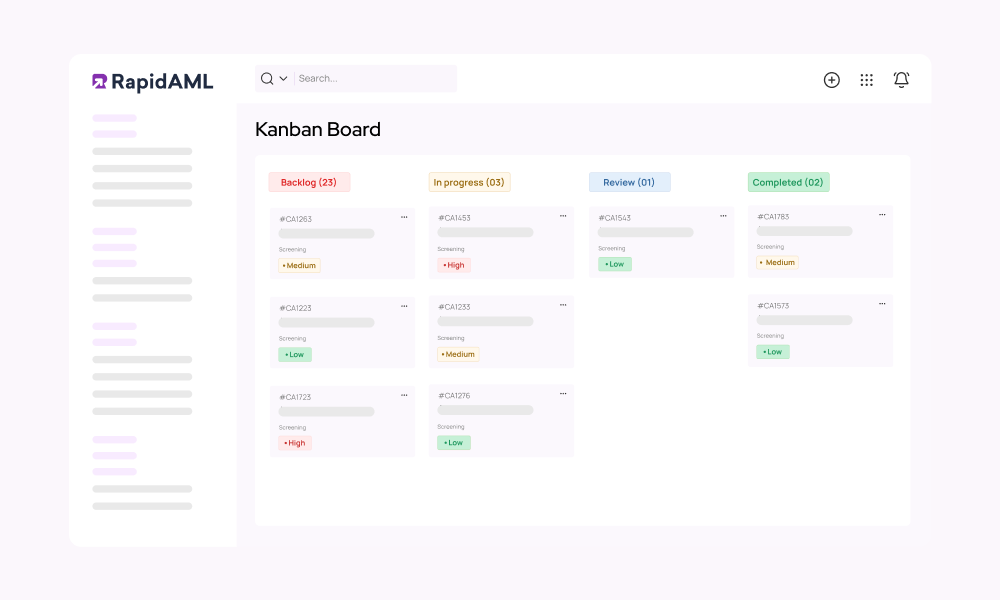
Case Management
Case Management Workflows So Good, They Practically Run Themselves
Don’t reinvent the wheel when RapidAML’s got you covered. No stepping on toes, no passing the buck, everyone knows their part with our role-based workflows. Intuitive consoles and effortless collaboration keep things flowing smoother than a perfect heist plan (minus the crime) with our smart case management.
Customer Risk Assessment
Build Customer Risk Profiles Like Writing a Biography
RapidAML creates customer risk profiles like a fine work of art. Precise, detailed and not a single stroke out of place.
Configurable risk parameters, a weightage methodology that’s more calculated than a chess grandmaster and an automated risk score calculated after factoring in Related Party risk scores.
With our AML risk assessment software, everything is accounted for, no spells needed!
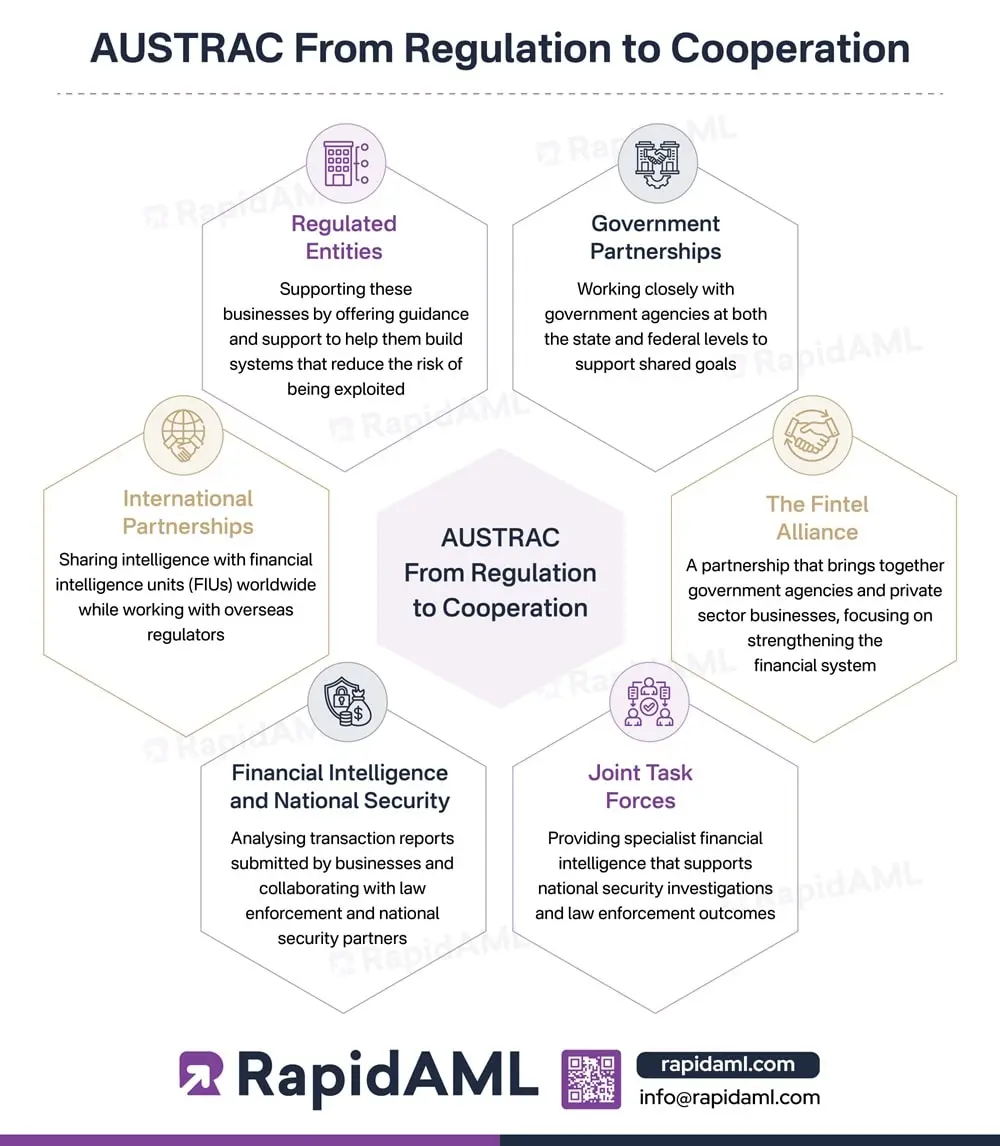
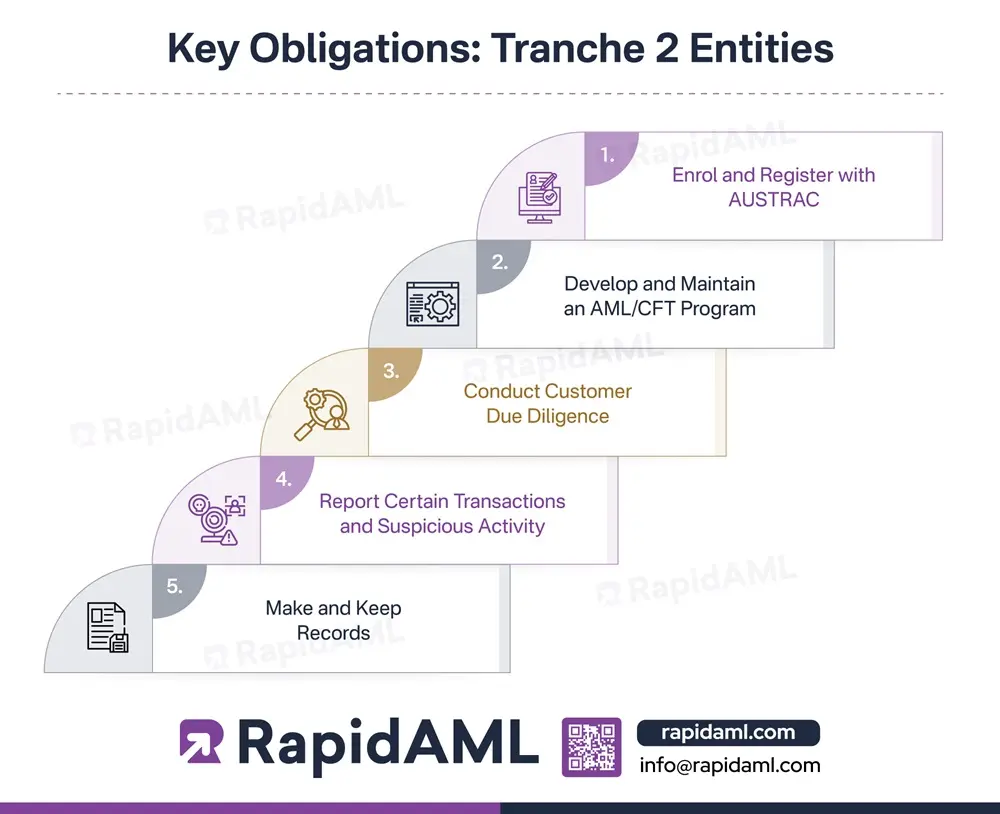
Regulatory Reporting
Elevate AML Regulatory Reporting with RapidAML for Unmatched Accuracy and Quality
With RapidAML, you get the best AML software that streamlines regulatory reporting with spot-on data collation, intuitive dashboards, and smooth workflows and submits reports on time. We keep everything neat with audit trails. No stress, just success!
Transaction Monitoring
Detect Suspicious Transactions in Real-Time with Our Transaction Monitoring
RapidAML runs on the fuel of next-gen tech, transaction monitoring technology faster than a hawk eyeing its prey, enabling real-time detection of suspicious transactions with configurable monitoring rules, customisable red flags, and automatic escalation for quick alert resolution.