
RapidAML Team
2024-06-18
Dealers in Precious Metals and Stones (DPMS) are prone to being drawn into money laundering schemes intentionally or unintentionally. For instance, criminals use their ill-gotten money to buy gold, diamonds, and other precious metals or stones, transferring the black money from their possession to the dealers. These criminals then sell the precious metals to someone else to bring the money into the financial markets again and label it legitimate or authentically earned. This money can later be used for various unlawful practices like terrorist financing or proliferation financing.
The United Arab Emirates has taken proactive measures to combat money laundering and terrorist financing. As part of the UAE government’s efforts to fight these financial crimes, Anti-Money Laundering (AML), Combating the Financing of Terrorism (CFT), and Counter-Proliferation Financing (CPF) regulations are issued. These regulations pave the way for guidelines issued by various supervisory authorities and best practices necessary to identify instances of financial crimes and mitigate the risks.
UAE Federal AML/CFT/CPF legislation places responsibility on all relevant persons in UAE to ensure the prevention, detection, and reporting of money laundering, terrorism financing, proliferation instances, and compliance with sanctions. The UAE Federal AML/CFT/CPF legislation includes:
The UAE is one of the biggest hubs for trading precious metals and stones. Dubai is recognised as one of the leading centres for gold and diamond trading. Dubai Multi Commodities Centre (DMCC), the UAE’s largest free-trade zone in the Jumeirah Lake Towers district of Dubai, is dedicated to facilitating various trades, including precious stones and metals. Considering the size of the precious metals and stones market, DPMS is often exploited by criminals to launder money.
Dealers in precious metals and stones (DPMS) play a significant role in the UAE’s economy. They undertake various activities related to precious metals and stones, from production to trading, establishing the UAE as an important regional hub for precious metals and stones. While DPMS play a pivotal role in shaping UAE’s economy, they also face various AML compliance challenges that must be addressed to prevent criminals from exploiting them.
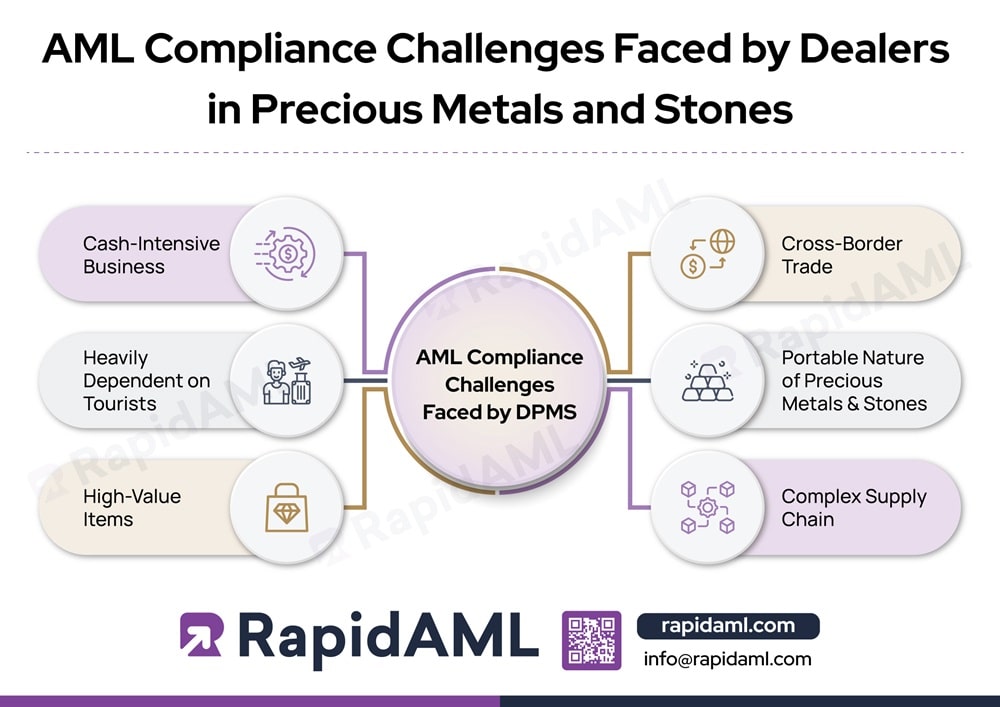
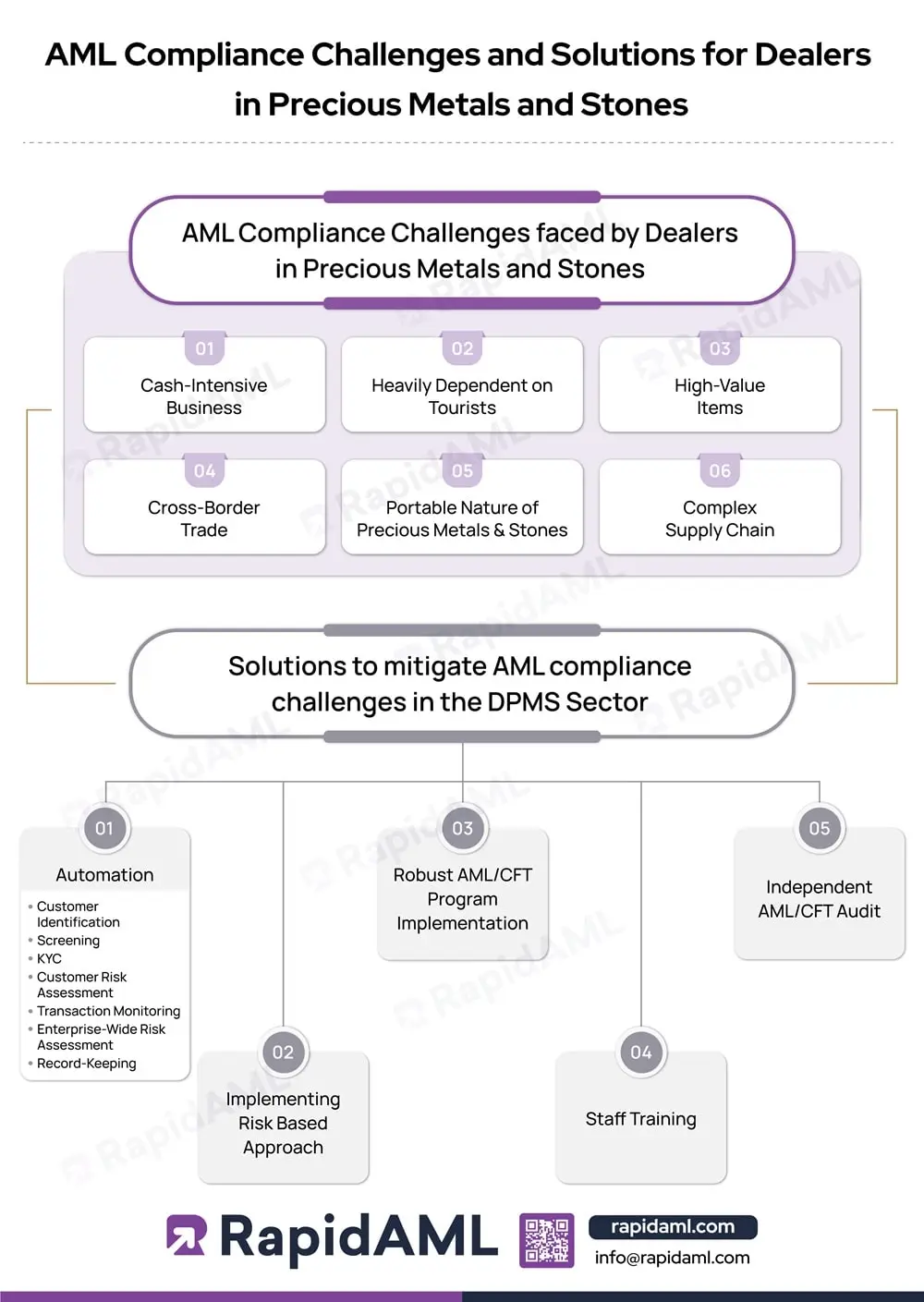
Cash-Intensive Business
A considerable amount of cash is involved in the trade of precious metals and stones. Due to its cash-intensive nature, it becomes difficult to trace the origin of funds and discover the money-laundering activities involved. Moreover, due to the high prices involved in a transaction of precious stones or metals, payments are bifurcated in cash, multiple money orders, cheques, or paid through a third-party account. This further complicates the identification process of probable money laundering.
Heavily Dependent on Tourists
The UAE is one of the most famous tourist destinations. The tourist industry contributes immensely to the DPMS sector’s customer base. However, the non-stationary nature of tourists creates a challenge to undertaking customer due diligence (CDD) processes and monitoring.
High-Value Items
Precious metals and stones are high-value commodities, making them attractive targets for money laundering activities. Since a large amount of money is required to trade in these stones and metals, criminals often pool their black money into it. Differentiating between a genuine buyer’s money and a criminal’s money becomes challenging.
Cross-Border Trade
Precious metals and stones are traded internationally from one country to another, which makes them a subject of cross-border trade. Every country has laws and legislations that apply to trade and businesses taking place on its soil. This can complicate AML compliance efforts due to the presence of various regulatory frameworks and jurisdictional challenges.
Portable Nature of Precious Metals and Stones
The portable nature of precious metals and stones makes them easy to carry from one place to another, enhancing the chances of illicit smuggling and illegal trade.
Complex Supply Chain
The DPMS Supply Chain can be complicated due to the presence of various parties and intermediaries involved in the trade. The involvement of multiple parties makes it difficult to ensure transparency or trace the origin of money laundering.
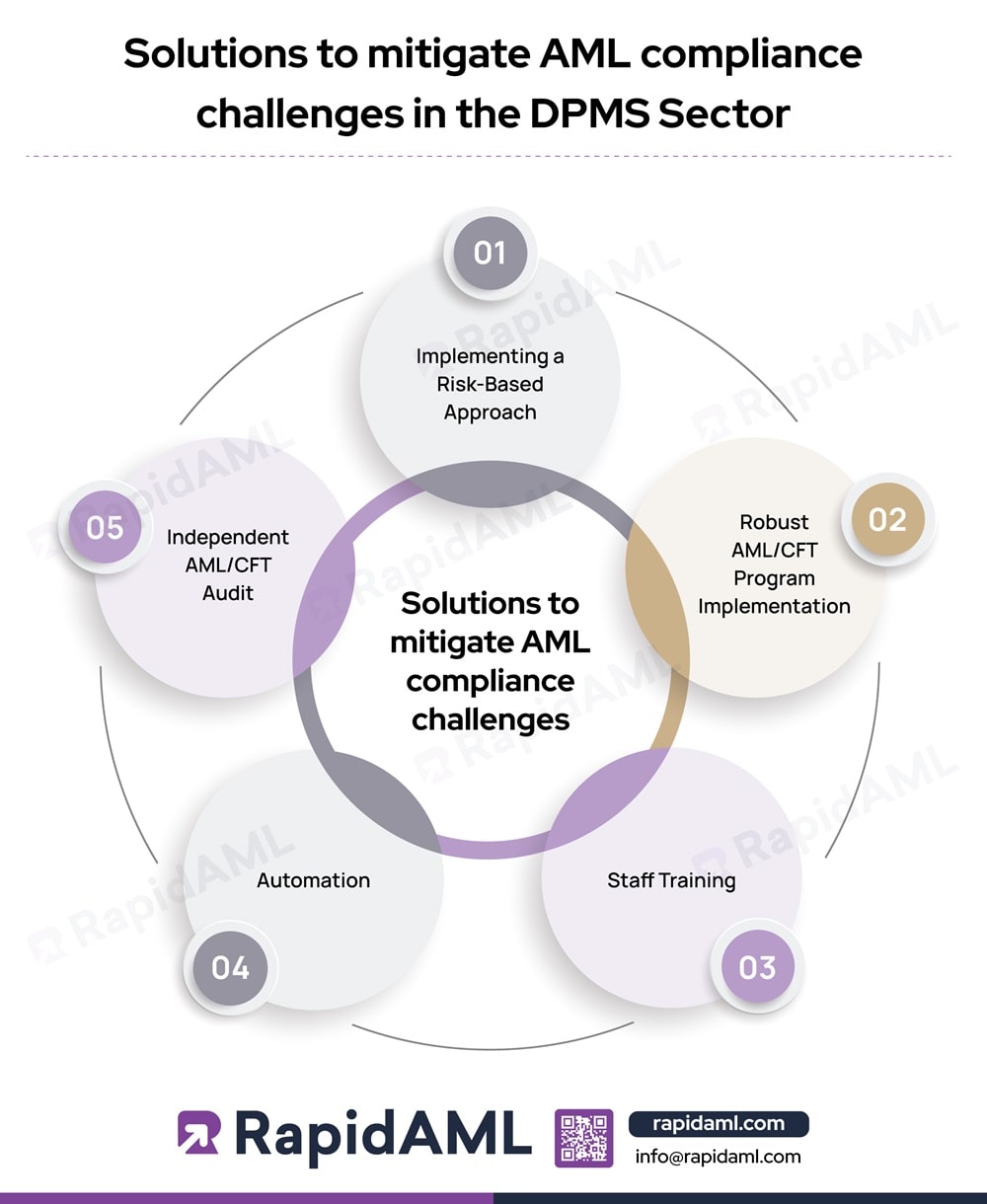
DPMS Entities must identify the risk and take measures to tackle the same. Since resources are always scarce, it is important that controls are prioritised according to the level of risks involved. Taking a risk-based approach (RBA) helps fight ML/TF risks in the most efficient way.
DPMS Entities must implement a comprehensive AML/CFT program that covers all necessary aspects like policies and procedures, business risk assessment, customer due diligence, transaction monitoring, reporting, etc.
DPMS entities must offer adequate training to their staff for compliance with all necessary procedures that ensure regulatory compliance. Effective AML compliance training should cover well-defined procedures, policies, and internal controls.
AML compliance challenges can be mitigated in the DPMS Sector through automation. Automation can help reduce the complexities that the DPMS sector faces while understanding AML regulations. Automation can help identify and report suspicious activities, streamline customer due diligence, and provide a centralised platform for managing AML compliance efforts to avoid non-compliance penalties.
Periodic and independent AML/CFT audits can help identify lacunas in policy and procedure and the effectiveness of controls so that continuous improvements can be made.
Conclusion
Money laundering is a serious crime and is no longer restricted to financial institutions or businesses. Rather, it includes precious metals and stones and many other non-financial businesses and professions. Black money is pooled into precious metals and stones. The smuggling, stealing, and trading of precious metals, stones, or gems generate funds. These funds generated from such unlawful activities are later on used for Anti-Money Laundering.
DPMS sector is prone to various criminal involvements due to its vast nature. This further leads to the sector facing multiple compliance challenges and risks associated with it. To deal with criminal involvement and ML/TF cases, implementation of AML/CFT measures, technological advancements, and risk-based approaches can contribute significantly. Further, mitigating AML compliance challenges in the DPMS Sector is crucial to ensure effective compliance with regulatory frameworks.
Pathik is a Chartered Accountant with over 26 years of experience in governance, risk, and compliance. He helps companies with end-to-end AML compliance services, from conducting Enterprise-Wide Risk Assessments to implementing robust AML compliance frameworks. He has played a pivotal role as a functional expert in developing and implementing RegTech solutions for streamlined compliance.
Pathik's expertise extends to guiding businesses in navigating complex regulatory landscapes, ensuring adherence to FATF and other international standards, and mitigating financial crime risks. He is a recognised thought leader in AML/CFT, frequently sharing insights on emerging compliance challenges on various platforms.
Join our Waitlist