
RapidAML Team
2024-05-17
It is important for Designated Non-Financial Businesses and Professions (DNFBPs) and Virtual Asset Service Providers (VASPs) to design their AML/CFT framework and implement AML/CFT policies and procedures to counter the risks of money laundering and terrorist financing. This article provides a detailed understanding of best practices for crafting effective AML/CFT policies and procedures.
AML policy is a formally drafted document approved by the senior management of an organisation. The AML policy lays down the procedures, steps, and methodologies to be utilised by the organisation for combating the instances of Money Laundering (ML), Financing Terrorism (FT) and Proliferation Financing (PF) of Weapons of Mass Destruction (WMD) to ensure compliance with the Federal Decree-Law No. 20 of 2018 on Anti-Money Laundering and Combating the Financing of Terrorism and the Financing of Illegal Organisations in the UAE.
The Designated Non-Financial Businesses and Professions (DNFBPs) and Virtual Asset Service Providers (VASPs) operating in the UAE are required to ensure compliance with the UAE federal laws designed to combat ML, FT and PF.
The Cabinet Decision No. 10 of 2019 on the Implementing Regulation of Federal Decree-Law No. 20 of 2018 and Combating the Financing of Terrorism and Illegal Organisations Guidelines for Designated Non-Financial Businesses and Professions require the DNFBPs and VASPs to have in place an AML/CFT program for mitigating ML/FT and PF risks.
The ML/FT and PF risk mitigation mechanism contains various types of documents, methodologies, and analyses regarding business risk assessment, customer onboarding and exit strategies, etc.
The cabinet decision and AML guidelines require DNFBPs and VASPs to document these ML/FT and PF risk mitigation measures deployed in proportion to the risk it is exposed to while considering the findings of the national risk assessment in formal internal documentation, usually known as AML/CFT policy.
These AML/CFT policies and their allied documents, such as procedures and controls, need to be made available to authorities as and when demanded, as the AML Policy substantiates and documents various measures implemented by the DNFBPs and VASPs to curb ML/FT and PF, examples of such measures include:
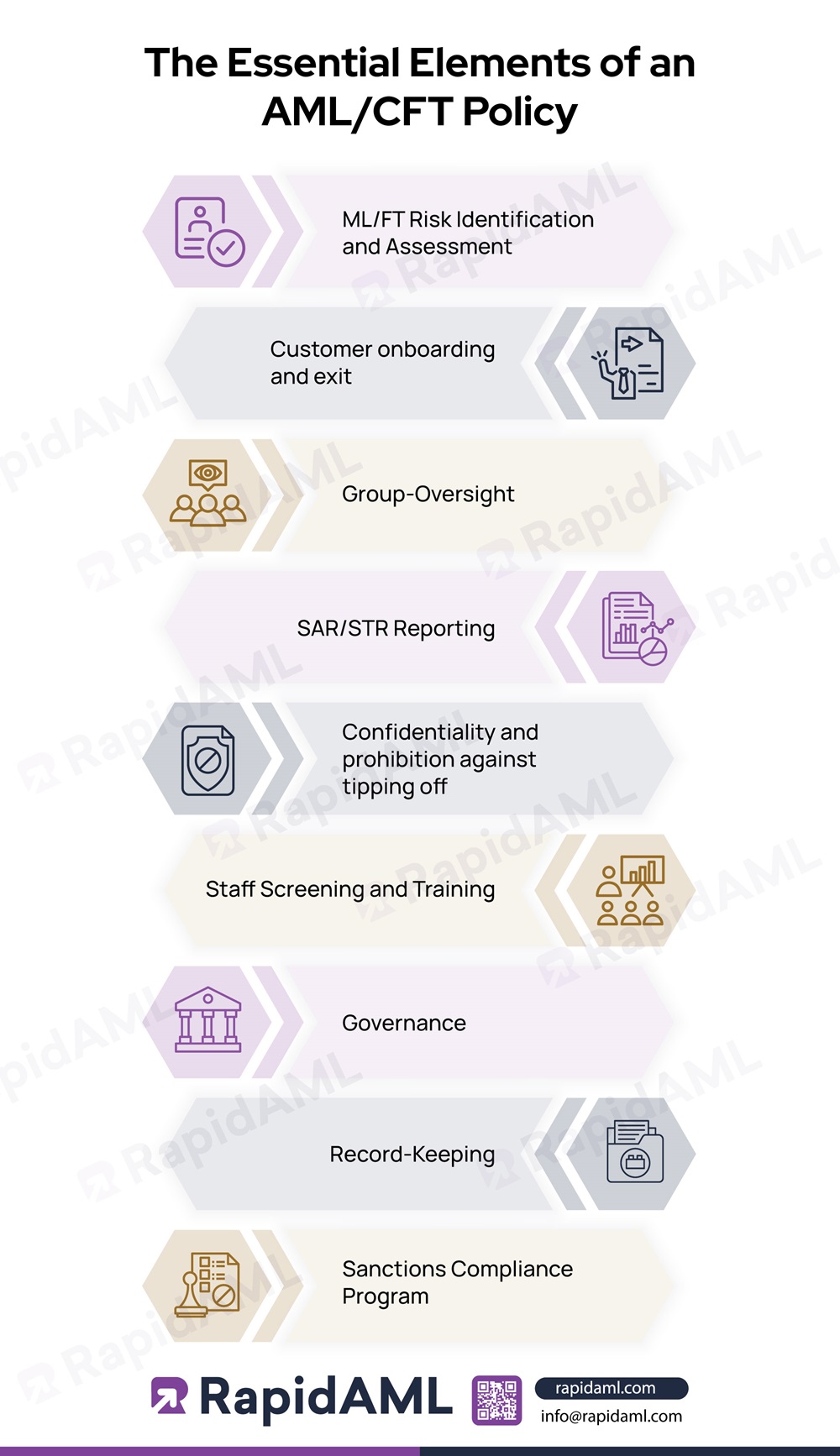
The essential elements of the generic AML/CFT policy applicable for DNFBPs and VASPs in UAE are discussed below as follows:
1. ML/FT Risk Identification and Assessment
The AML/CFT policy should be formulated using a Risk-Based Approach (RBA), which means that AML/CFT measures must be proportional to the ML/FT and PF risks to which it is exposed.
The AML/CFT policy document must enable the staff of the DNFBPs and VASPs to understand and identify the ML/FT typologies according to their sector, such as Virtual Assets (VA) related red flags for VASPs, precious stones and metals-related red flags for dealers in precious metals and stone, etc., and the risk factors that expose their business to ML/FT and PF (such as customers, geography, delivery channel, etc.).
The AML/CFT policy must be formulated, considering these risk factors, and the inherent risk must be assessed. The policy must elaborate on qualitative and quantitative risk mitigation measures to reduce the inherent risk, and the procedures and controls to address the same must be outlined.
The AML/CFT policy must clearly state the means or tools relied upon for risk Identification. It must also chart out the tentative organisational roles around risk identification, reporting of suspicious activities and transactions, and tools and procedures relied on for the same. The policy must include imparting staff training for the same and clearly establishing alert escalation and investigation timelines.
Procedure: The procedural part of the policy must address the risk identification and assessment component by setting down steps and procedures for carrying out the enterprise-wide risk assessment that considers business relationship-specific risk, geographic risk, product/service, transaction-based risk, channel-related risk, new technology-related risk, tax crime-related risk, and other risk factors. It must also mention risk assessment methodology.
2. Customer Onboarding and Exit
The AML/CFT policy for DNFBPs and VASPs must have clearly outlined instructions regarding the circumstances and timing of conducting the following customer onboarding practices:
3. Group-Oversight
Group oversight refers to DNFBPs and VASPs having uniform and consistent AML/CFT policies and procedures across their branches, subsidiaries or group companies located in and outside the UAE. The DNFBPs and VASPs in UAE need to ensure that the AML/CFT policies and procedures are consistent with UAE federal laws. The group-wide AML/CFT policies should ideally include the following:
4. SAR/STR Reporting
The AML/CFT policies and procedures should ideally contain steps and processes for conducting internal investigation of potentially suspicious activities and transactions by the employees or compliance team to the compliance officer prior to filing official (suspicious activity report/ suspicious transaction report) SAR/STR on the goAML portal. The filing of SAR/STR is a statutory obligation. Failure to report suspicion results in fines and penalties. The AML/CFT policies should ideally contain points discussed as follows:
Such policies must be communicated to appropriate employees within the organisation, documented, and approved by senior management.
5. Confidentiality and Prohibition against Tipping Off
The AML/CFT Policies, procedures, and controls must provide for the confidentiality and protection of customer information contained in SARs/STRs. Any suspicion about the customer must not be informed to the customer themselves as it would amount to ‘tipping off’, which is punishable under UAE federal laws. Appropriate and adequate access rights need to be mentioned in the AML/CFT policy for staff using core AML/CFT systems for case management and defining notification recipients for the same. The AML/CFT policies and procedures must also mention how the flow of information takes place with the regulator. The AML/CFT policy must provide for training to client-facing staff in this regard.
6. Staff Screening and Training
An essential element of AML/CFT policies and procedures for DNFBPs and VASPs is to have defined staff screening and training procedures and requirements in place. Such staff training must ideally include educating the staff about:
Such training programs must be based on staff competency, the delivery channel, the training content, and the frequency of training. Ideally, the content of training would differ for the client-facing staff, the compliance team, and senior management, educating each category on the scope of their individual roles and responsibilities to curtail ML/FT and PF. The policy must also discuss how it Identifies, manages, and deploys training resources for its staff.
7. Governance
The AML/CFT policies and procedures of DNFBPs and VASPs must contain the governance structure of the business. The AML/CFT policy must provide for the appointment of a competent compliance officer and chart out the responsibilities of senior management, especially regarding granting approvals prior to commencing business relationships with high-risk customers such as Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs). The AML/CFT policy must outline the powers of the audit function with regard to assessing the quality, efficiency, adequacy and appropriateness of the AML/CFT policy.
8. Record-Keeping
The AML/CFT policy of DNFBPS and VASPs must ideally contain the scope for maintaining, organising and retaining records and documents pertaining to:
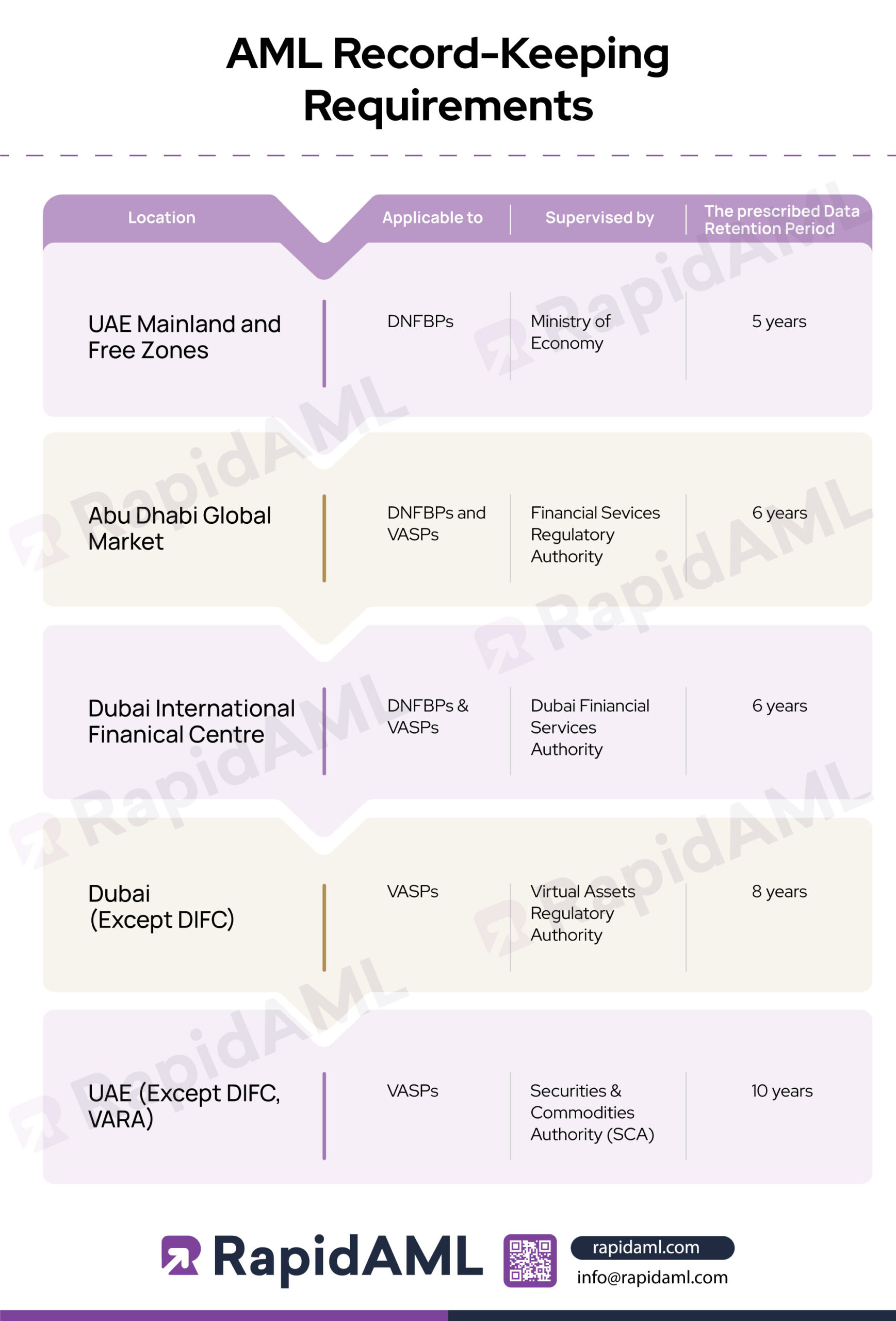
| Sr. No | Area of Operation | Applicable to | Supervisory Body | Prescribed Data Retention Period |
| 1 | UAE Mainland and Free Zones | DNFBPs | Ministry of Economy | Five [5] years |
| 2 | Abu Dhabi Global Market | DNFBPs & VASPs | Financial Services Regulatory Authority | Six [6] years |
| 3 | Dubai International Financial Centre | DNFBPs & VASPs | Dubai Financial Services Authority | Six [6] years |
| 4 | Dubai (Except DIFC) | VASPs | Virtual Assets Regulatory Authority | Eight [8] years |
| 5 | UAE (Except DIFC, VARA) | VASPs | Securities & Commodities Authority (SCA) | Ten [10] years |
Procedures: The types of records needed, customer information, third-party CDD, ongoing monitoring, SAR/STR reports, training logs, etc., must be maintained in given formats.
9. Sanctions Compliance Program
The AML/CFT policy for DNFBPs and VASPs must maintain records of sanctions and targeted financial sanctions lists subscribed.
Procedures: Implementation steps, software tools used, APIs utilised, etc., are to be mentioned in the procedure escalation hierarchy.

1. Creating a b Compliance Team
To create an effective AML/CFT policy, the DNFBPs and VASPs need to ensure that their team of compliance personnel is competent to develop an AML/CFT policy that is adequate and proportional to their business’s exposure to risks. The compliance team must be b and well-versed in the latest trends and amendments in the UAE federal laws and international regulations for curbing ML/FT and PF.
Having a b compliance team will ensure the effective implementation of the AML/CFT policy and the timely, effective, and accurate fulfilment of the AML/CFT obligations of DNFBPs and VASPS.
2. Risk-Based Approach
The AML/CFT policy for DNFBPs and VASPs must be crafted by taking into consideration the various kinds of ML/FT and PF risks to which the business is exposed. The AML/CFT policy must be just right for the business; it should not be overly stringent, leading to difficulty in conducting business and higher costs, nor the AML/CFT policy should be under-compliant, leading to cracks or loopholes that criminals can take advantage of while conducting business with such DNFBP or VASP. Ideally, the AML/CFT policy needs to be the perfect blend of adequate compliance measures, considering a variety of risk factors, each identified, assessed and mitigated appropriately.
3. Identify Applicable Regulations Locally and Globally
The AML/CFT policy must be crafted while considering the crucial component of ensuring adequate compliance with applicable laws and regulations, both on a local and international basis.
The DNFBPs and VASPs need to consider the applicable supervisory authority and rules issued in regard to curbing ML/FT/PF, such as the DFSA, ADGM, or VARA. At the same time, the DNFBPs and VASPs should also consider the laws of other countries in which they are operating and the relevant AML/CFT measures prescribed. Whether such measures are at par with FATF standards or not should be considered, and if such measures are sub-standard to FATF recommendations, the DNFBPs and VASPs must formulate their policies by covering for these deficiencies for their branches, subsidiaries, and third parties operating outside UAE.
4. Define the Methodology for Screening, Monitoring, and Identification of red Flags
The AML/CFT policy crafted is only as effective as the processes, methodologies, steps and measures prescribed within. The AML/CFT policy needs to clearly define the manner in which the business is required to conduct various kinds of name screening, ongoing monitoring and identification of AML/CFT typologies. The DNFBPs and VASPs must also seriously consider relying on AML/CFT software, automation tools, APIs, etc., to reduce costs, streamline compliance and operational processes, automate mundane and repetitive tasks, and send alerts when any red flags are identified.
5. Reporting Mechanisms
The effectiveness of an AML/CFT policy is usually gauged by its ability to educate and enable customer-facing staff, compliance officers, and senior management to actively participate in identifying suspicious activities or transactions related to ML/FT and PF. The AML/CFT policies, procedures, and controls must provide the formats, escalation methods, and internal reporting mechanisms and steps prior to the official filing of SAR/STR and define timelines on the goAML portal.
6. Review Performance by Conducting Audits
The effectiveness and accuracy of the AML/CFT policy in the context of its compliance with regulatory requirements can be assessed only by conducting frequent and unbiased AML/CFT policy audits. An Independent audit function must conduct such audits to test the efficiency, adequacy and accuracy of internal policies, procedures, and controls. If any deficiencies are found, senior management must remedy such deficiencies as soon as possible.
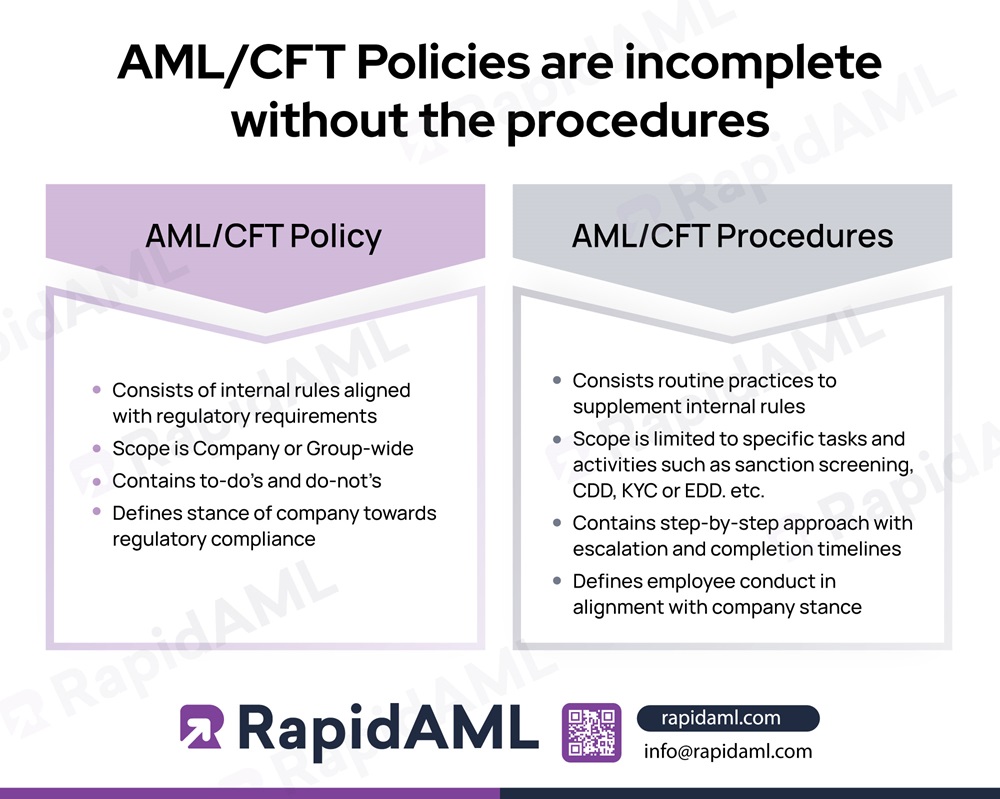
AML/CFT Policies are official documents that establish internal rules for the business to follow for ensuring continuous compliance with relevant laws.
AML/CFT Procedures define and state the individual roles and responsibilities to ensure that the policies’ provisions are complied with in totality. They also prescribe the use of tools, software, or mechanisms to establish and ensure control over policies and procedures. In simple terms, policies establish internal rules and procedures specify who shall do what task and in what manner.
AML/CFT procedures clarify the management objectives and processes involved in ensuring compliance with the AML/CFT policy.
AML/CFT procedures clarify and shape employee conduct and behaviour in accordance with the AML/CFT policy by setting the tone of how compliance processes and activities shall be carried out within the organisation.
The procedures govern how compliance with the policy is achieved; for example, defining the steps for performing the name screening process and elaborating on the methodology and tools used for name screening would aid with compliance with policy requirements related to name screening. The procedures would contain a step-by-step guide on how to conduct name screening, which tool to use, how to record and report various outcomes, when and to whom to escalate the case, etc. The AML/CFT policies are incomplete without the procedures that map out the steps to be carried out by the staff of the business to ensure its compliance with regulations as given in the policy.
Crafting effective AML/CFT policies, procedures, and controls to achieve adequate ML/FT and PF risk mitigation is an essential requirement for DNFBPs and VASPs operating in the UAE.
AML/CFT policies, procedures, and controls are to be carefully drafted, keeping in mind the individual business needs according to the nature and size of operations, the industry-specific AML/CFT compliance requirements (such as VASPs, Real-Estate, Gold sector, Legal services providers, etc.), and region/supervisory body-specific AML/CFT rules (such as DFSA, FSRA, VARA, etc.). The AML/CFT policy for VASPs and DNFBPs would differ significantly according to their respective AML compliance requirements. However, the fundamental requirements of adherence to federal laws offer certain uniformity, as discussed in the article above.
The AML/CFT policies, procedures, and controls should ultimately ensure relevance to the business for which they are being crafted to adequately mitigate ML/FT and PF risks.
Jyoti is a Chartered Accountant and Certified Anti-Money Laundering Specialist (CAMS), having around 7 years of hands-on experience in regulatory compliance, legal advisory, policy-making, tax consultation, and technology project implementation.
Jyoti holds experience with Anti-Money Laundering regulations prevalent across various countries. She helps companies with risk assessment, designing and deploying adequate mitigation measures, and implementing the best international practices to combat money laundering and other financial crimes.
Solutions
Services
Industries
Lorem Ipsum
Lorem Ipsum
Lorem Ipsum
Lorem Ipsum
Lorem Ipsum
© RapidAML 2025
Solutions
Transaction Monitoring
Regulatory Reporting
Services
AML/CFT Health Check
Industries
Lorem Ipsum
Lorem Ipsum
Lorem Ipsum
Lorem Ipsum
Lorem Ipsum
© RapidAML 2025
Contact Us