
RapidAML Team
2024-05-17
Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) plays a vital role in countering financial crimes like Money Laundering, Financing Terrorism, and Proliferation Financing (ML/FT and PF). Regulated entities take EDD measures while onboarding customers (including natural or legal persons, suppliers, business partners, or associates). Let us first understand what Customer Due Diligence (CDD) is to appreciate the difference between CDD and EDD.
Customer Due Diligence (CDD) contains steps that aid Designated Non-Financial Businesses and Professions (DNFBPs) in identifying their customers, verifying their identities, and assessing the money laundering risks posed by such customers to their business. Implementation of a CDD process helps businesses guard against potential fraud and fulfil regulatory compliance requirements as required by the UAE federal laws. Implementation of an effective and compliant CDD program helps DNFBPs to ensure that their business is not utilised as a vehicle to launder illicit proceeds by criminals by identifying such criminals at the customer onboarding stage.
EDD, in alignment with existing CDD measures, calls for businesses to take additional or extra measures to identify and mitigate the risk posed by high-risk customers. EDD measures constitute obtaining thorough and complete knowledge regarding the customer, their businesses, and financial standing, as well as understanding the purpose behind transactions while ensuring that such high-risk customer profiles are monitored on a regular basis and kept up-to-date with regulatory requirements.
In simple terms, the EDD process, as prescribed under UAE federal laws and guidelines for DNFBPs, generally involves stricter implementation of CDD measures that include components such as follows:
The DNFBPs operating in the UAE are required to have an AML/CFT program which contains policies, procedures, systems and controls specifying the implementation of EDD measures based on a risk-based approach (RBA) recommended by the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) to which the UAE is a signatory. The DNFBP’s policies and procedures must clearly mention the procedures around EDD implementation, such as follows:
Know Your Customer, Know Your Risks
EDD Is Your First Line of Defence
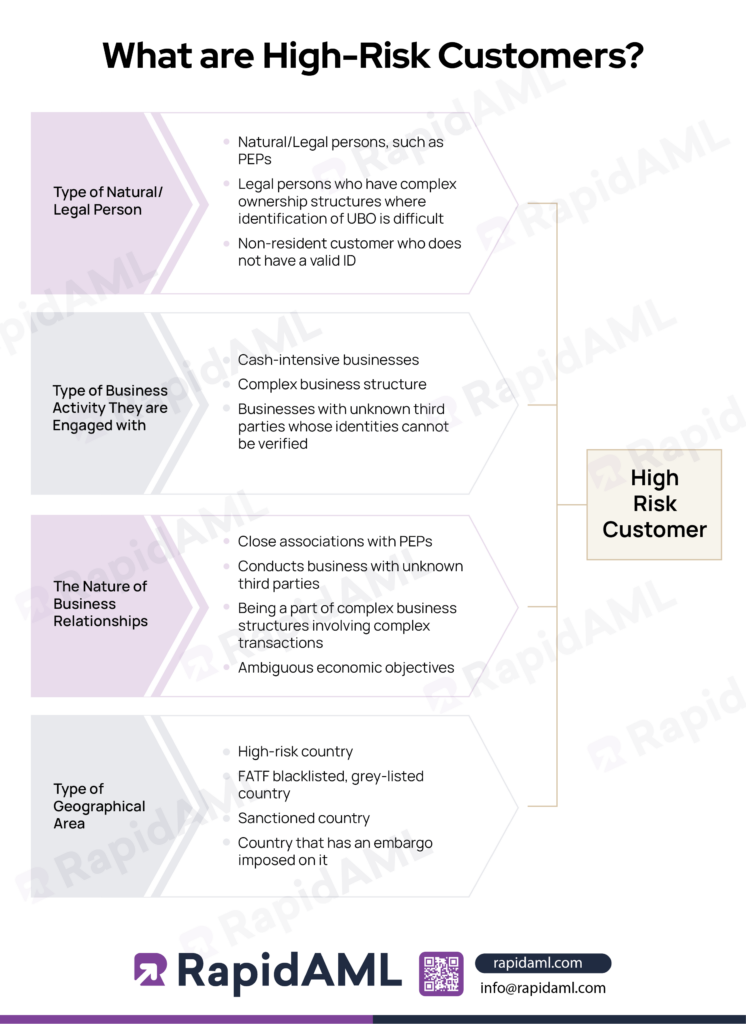
Any customer who brings along or denotes risk due to:
are known as high-risk customers.
DNFBPs in the UAE are required to undertake EDD measures in the situations listed below:
In all situations where EDD measures are applied, DNFBPs are required to ensure that reasonable, appropriate, and adequate measures are taken to collect customer information to carry out EDD proportionate to the degree of ML/FT and PF risks to which the business is exposed.

The DNFBPs are required to formulate their AML/CFT compliance policies, procedures, systems and controls to ensure compliance with the UAE federal laws and FATF recommendations. An effective AML/CFT compliance program must contain steps for carrying out EDD as mentioned below:
1. Gathering Additional Information for Identity Verification
Once it is determined that EDD is required to be carried out for a customer, the DNFBP is required to seek additional information from the customer, such as follows:
2. Source of Funds and Source of Wealth
The next step involves ascertaining the sources of funds and source of wealth information for the transaction and collecting the documentation for the same, which includes:
a. Source of Funds: establishes the origin of funds involved in the transaction; examples include:
i. Salary or bank statements;
ii. Profit and loss statement;
iii. Loan approval documents, funds lying in escrow account;
iv. Savings, pension, interest on savings;
v. Incomes such as profession, lottery, compensation, etc.
b. Source of Wealth: establishes how wealth/assets were acquired over a period of time or what is the net worth of the customer; examples include:
i. Documents denoting title to assets owned;
ii. Trust deeds indicating income or capital generated;
iii. Audited financial statements and tax returns;
iv. Gift deed, Inheritance received.
3. Payment from the Customer’s Own Bank Account
As a safe practice, DNFBPs must insist high-risk customers complete the transaction using their own bank account.
4. Top Management Approval
Additionally, senior management approval must be sought to ensure that high-risk customers are onboarded considering the risk appetite of the entity.
5. Enhanced Monitoring
After obtaining senior management approval for establishing a business relationship, the next step is to deploy enhanced monitoring measures, such as ongoing sanctions screening and adverse media alerts, to regularly monitor the degree of risk posed by the high-risk customer so that the EDD measures can be adjusted and further information can be sought if the customer’s situation changes. In the context of virtual assets or wire transfers, red flags related to such transactions can be analysed while carrying out ongoing monitoring of transactions.
6. Periodic Review and KYC Refresh
This step requires the DNFBPs to conduct periodic reviews of customer profiles under EDD to ensure that the KYC information is refreshed as and when there is a change in information and at regular intervals to ensure continuous and timely updation of customer details.
7. Reporting Suspicious Activities and Transactions
If, while carrying out the EDD process as mentioned in the steps above, any unusual activity, deviations, or transactions are observed, reporting such suspicious activity or transaction on the goAML portal to the Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU) is mandatory. Failing to report suspicious activity or transactions will result in a breach of UAE federal laws and will attract punitive fines, penalties, and even imprisonment in certain cases.
A Stitch in Time Saves Nine
Catch Potential Risks before They Escalate
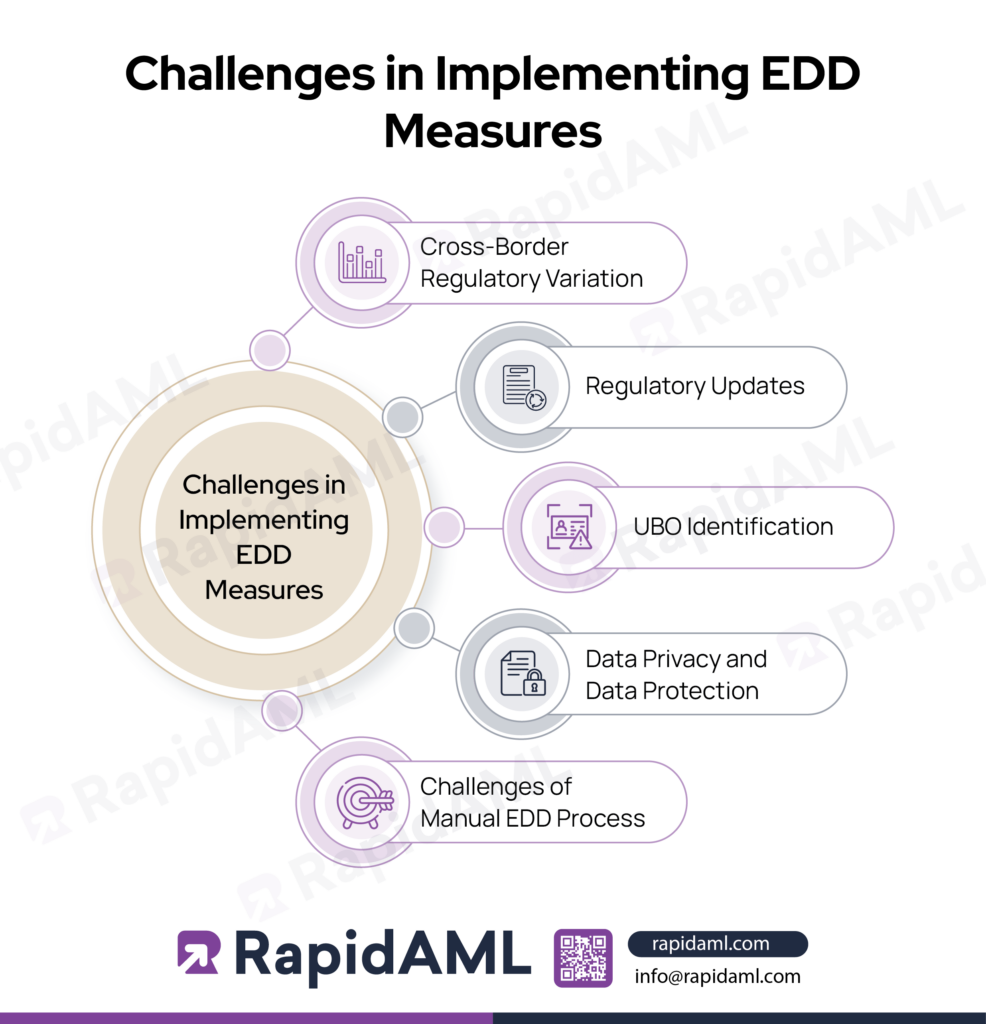
Some of the common challenges that crop up while implementing EDD measures are discussed below as follows:
Cross-border Regulatory Variation
The challenge of cross-border regulatory variation comes up when the DNFBP has its business operations in multiple jurisdictions, and each jurisdiction has distinct customer onboarding and EDD requirements. It is important for such a DNFBP to ensure that its EDD process is streamlined across jurisdictions to avoid breaches of regulatory requirements.
Regulatory Updates
The EDD procedures deployed by a DNFBP must be updated regularly to ensure continuous compliance with the frequent regulatory updates. Not updating AML/CFT policies and procedures in a timely manner would lead to potential non-compliance with updated regulations.
UBO Identification
The inability to ascertain the UBO of a legal person poses a huge challenge to DNFBPs due to opaque corporate structures, complex chains of ownership, and the existence of shell companies, tax havens, and offshore bank accounts. This leads the EDD process into a lengthy investigation with no definite conclusion as to the identity of the UBO.
Data Privacy and Data Protection
When it comes to collecting and storing the customer’s personal data, the DNFBP is required to ensure that it obtains consent to do so from its customer in an explicit manner by publishing the use and storage of data for the regulatory compliance process and ensuring compliance with the UAE and global data protection regulatory requirements.
Challenges of Manual EDD Process
Some of the challenges faced by DNFBPs when conducting EDD processes manually are listed as follows:
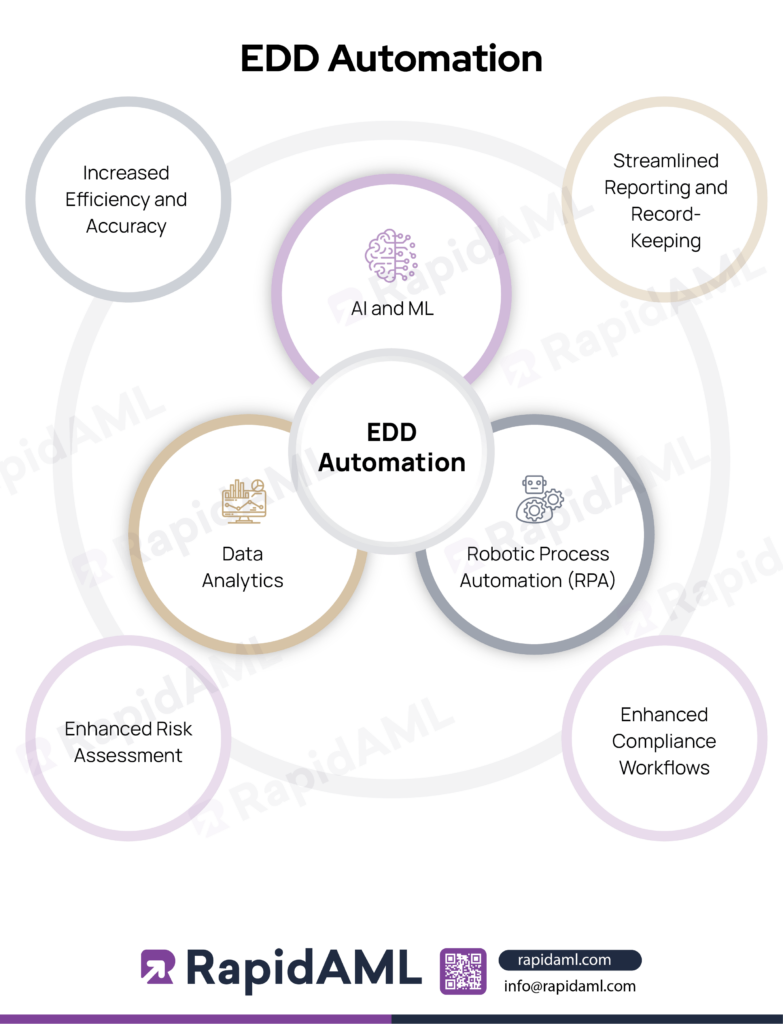
UAE federal law explicitly recommends that DNFBPs use technology to streamline their AML compliance process. EDD automation is one such tool that enables DNFBPs to carry out customer identification and verification, risk assessments, additional data seeking, and case management, specifically fulfilling EDD requirements.
Role of AI and ML
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) play a significant role in the automation of the EDD processes. AI and ML can help with carrying out various repetitive tasks such as customer identification and verification and assigning risk ratings based on the automation part of AI and the self-evolving feature of ML. AI and ML help customise the adverse media screening, PEP screening, and sanction screening process according to the needs of the DNFBPs.
Role of Data Analytics
Data analytics helps in deriving insights and drawing connections to ascertain the nature of complex business structures and identify UBOs. It also enables DNFBPs to identify risks and trends of high-risk customers.
Role of Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
RPA enables DNFBPs to automate repetitive tasks that involve sequential steps such as clicking, selecting from the drop-down menu, etc., involved with EDD processes such as sending notifications requesting additional information to customers and automating data entry components for various records and reports. This results in lesser human involvement and reduced man-hours behind repetitive tasks. The RPA, while using AI and ML, can automate processes such as:
The benefits of relying on EDD Automation are multifold. Some of the benefits are listed below:
The failure of DNFBPs to ensure compliance with the EDD requirements results in a breach of UAE AML federal laws and regulations, leading to fines, penalties, and even imprisonment or a ban from conducting business in certain cases. The loss of reputation and brand trust is an unpleasant consequence.
The DNFBPs in UAE, by adhering to EDD requirements prescribed by Federal laws, sector-specific guidelines, and FATF recommendations, can ensure that criminals involved in ML/FT and PF activities do not use DNFBP’s business as a vehicle to further their criminal activities.
Relying on technological advancements such as EDD automation is the need of the hour as manual processes are outdated, time-consuming, and less efficient, rendering them obsolete. On the other hand, the ability of EDD solutions to be customised in accordance with the business’s RBA to meet its specific individual needs, its scalability, customisation, and versatility to be integrated with other AML compliance solutions and operational solutions make EDD automation the ideal choice for DNFBPs intending to ensure continuous EDD compliance in UAE.
Risks Hide in Quiet Corner
Where Diligence Is Absent, Danger Finds Room to Grow

Purva is a Certified Anti-Money Laundering Specialist (CAMS) and a Lawyer with 5+ years of experience.
She has substantial knowledge of Anti-Money Laundering Laws, Rules, Regulations, and AML Compliance Processes. Purva has been instrumental in drafting RegTech processes, corporate policymaking, and fulfilling various legal research and drafting requirements arising from AML laws and regulatory technology.
Solutions
Services
Industries
Lorem Ipsum
Lorem Ipsum
Lorem Ipsum
Lorem Ipsum
Lorem Ipsum
© RapidAML 2025
Solutions
Screening
KYC
Customer Risk Assessment
Case Management
Transaction Monitoring
Regulatory Reporting
Services
Enterprise-Wide Risk Assessment
AML/CFT Health Check
Industries
Lorem Ipsum
Lorem Ipsum
Lorem Ipsum
Lorem Ipsum
Lorem Ipsum
© RapidAML 2025
Get Started
Contact Us